Akkermansia muciniphila
Akkermansia
muciniphila
Leading a New Era of Gut Health
Akkermansia muciniphila is the pioneer of next-generation probiotics
It has been widely recognized to play a role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier
Key role in regulating host metabolism and promoting immune balance
Akkermansia muciniphila is a pioneer of next-generation probiotics and has been widely recognized for its key role in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, regulating host metabolism and promoting immune balance.
Akkermansia muciniphila
Akkermansia muciniphila is a Gram-negative, anaerobic bacterium that inhabits the mucus layer of the human intestine.
This strain was first isolated in 2004 and belongs to the phylum Verrucomicrobia.
It plays a key role in regulating host metabolism and maintaining intestinal mucosal stability.
Akkermansia muciniphila is a Gram-negative, anaerobic bacterium that inhabits the mucus layer of the human intestine. This strain was first isolated in 2004 and belongs to the phylum Verrucomicrobia. It plays a key role in regulating host metabolism and maintaining intestinal mucosal stability.
Health Benefits
Stimulates GLP-1 Secretion
Enhances Gut Barrier Integrity
Upregulates tight junction proteins and mucus layer regeneration.
Modulates Inflammation
Reduces systemic and local gut inflammation.
Improves Lipid and Glucose Metabolism
Shown to reduce liver fat accumulation and blood glucose in preclinical and clinical studies.
Research Insights
Retains biological activity after pasteurization
Pasteurized Akkermansia strains have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. (Depommier et al., Nat Med, 2019)
Demonstrates a Significant Inverse Association With Obesity Risk
The Akkermansia content in feces was significantly negatively correlated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. (Dao et al., 2016)
Helps promote liver lipid metabolism and improve metabolic steatohepatitis (MAFLD)
Oral administration of Akkermansia reduces liver fat accumulation and inflammation in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NASH). (Everard et al., 2013)
Has the potential to improve the success rate of cancer immunotherapy
This bacterium is a microbial biomarker for tumor immunotherapy response and is positively correlated with the treatment response of cancer patients. (Routy et al., 2018)
The World’s Largest Akkermansia muciniphila Bioresource: Driving Probiotic Discovery
Akkermansia muciniphila
The world's largest bacterial strain resource library
Initiating a Breakthrough in Probiotic Innovation
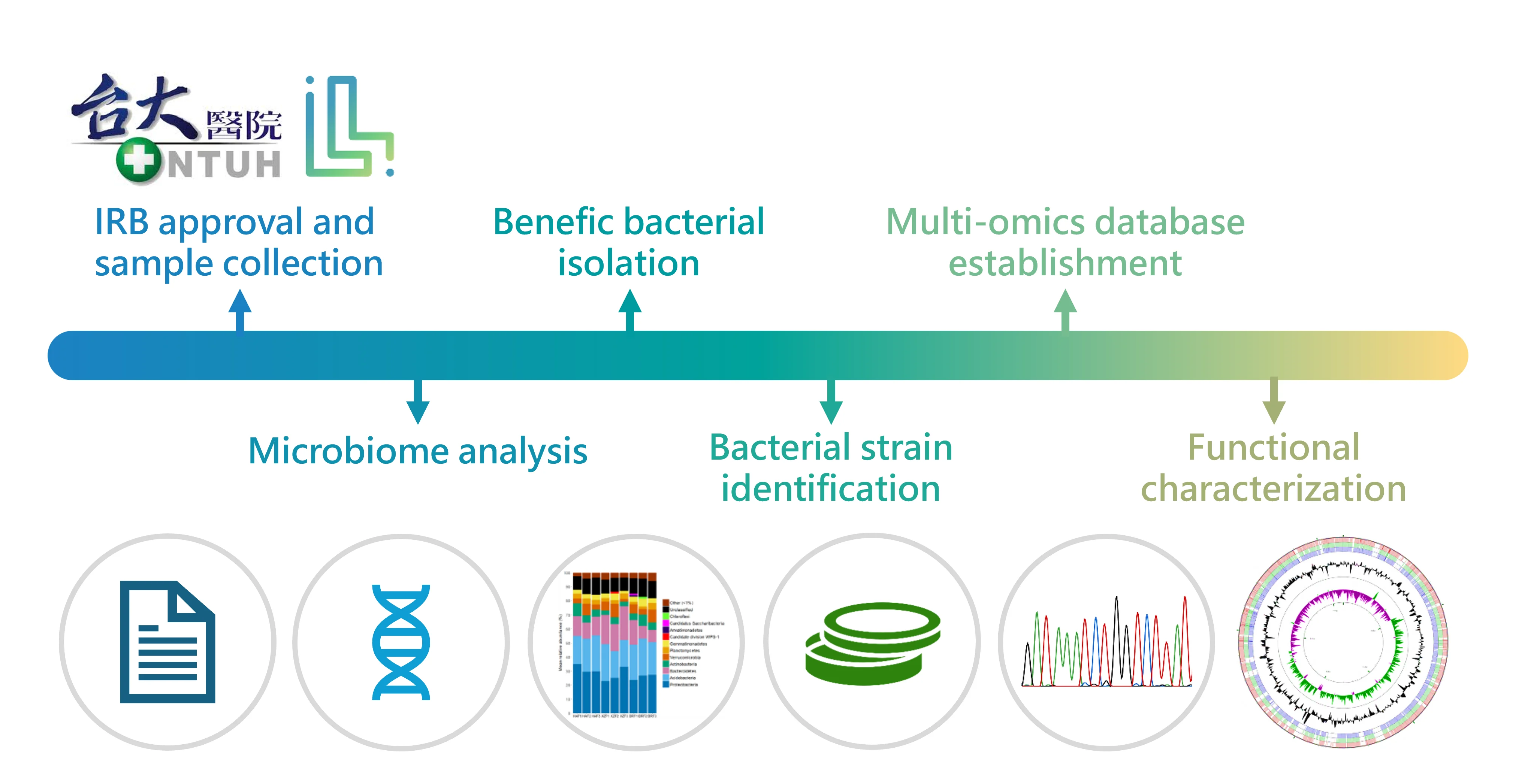
Leeuwenhoek collaborated with the National Taiwan University Hospital to isolate Akkermansia muciniphila from the intestines of healthy Taiwanese people and established a local bacterial strain library, which has now become the world's largest bacterial strain database for this bacterium.
From Genes to Functions, Fully Understand the Potential of Strains
From genes to functions
Fully understand the potential of strains
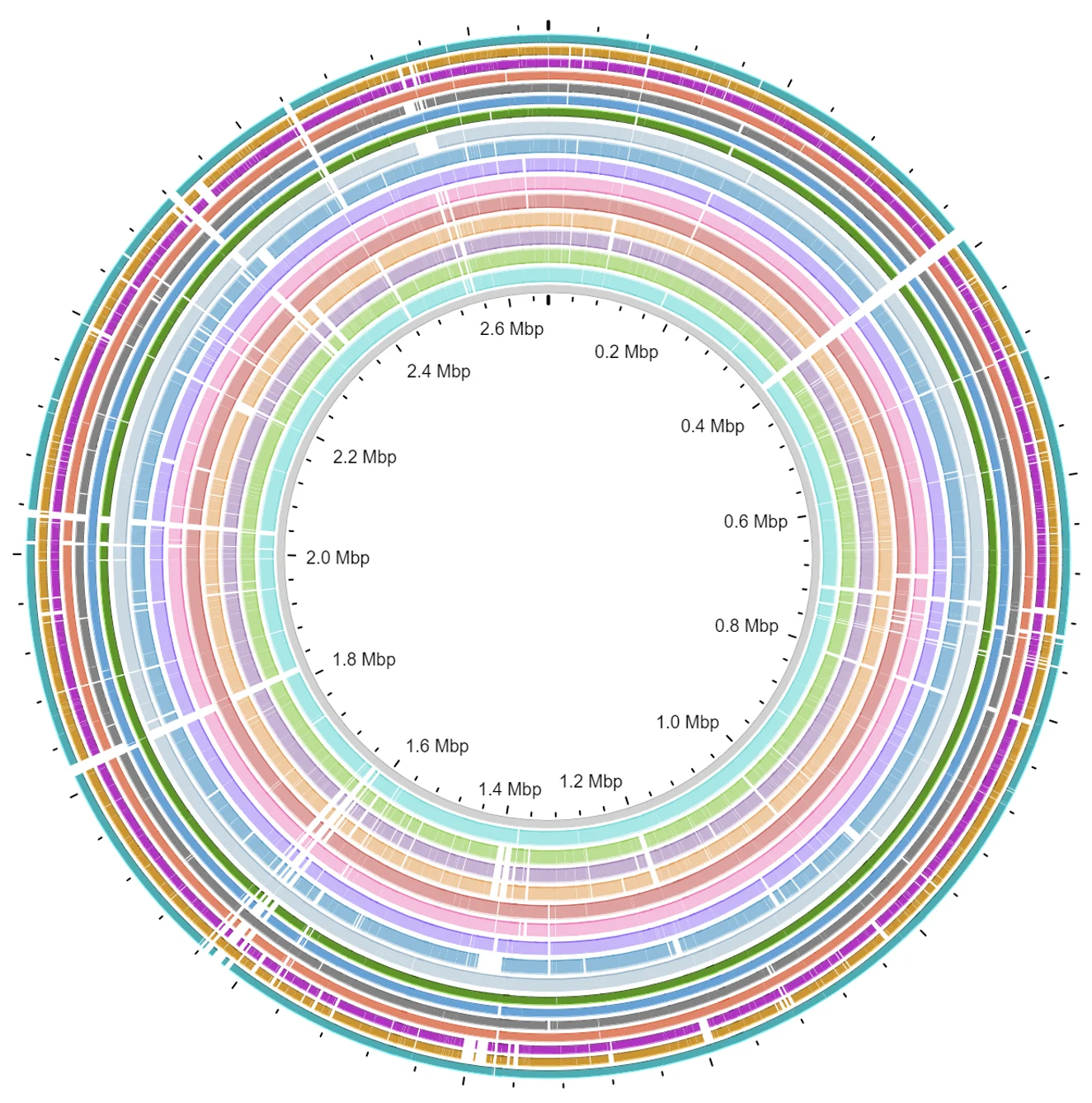
Whole Genome Sequencing
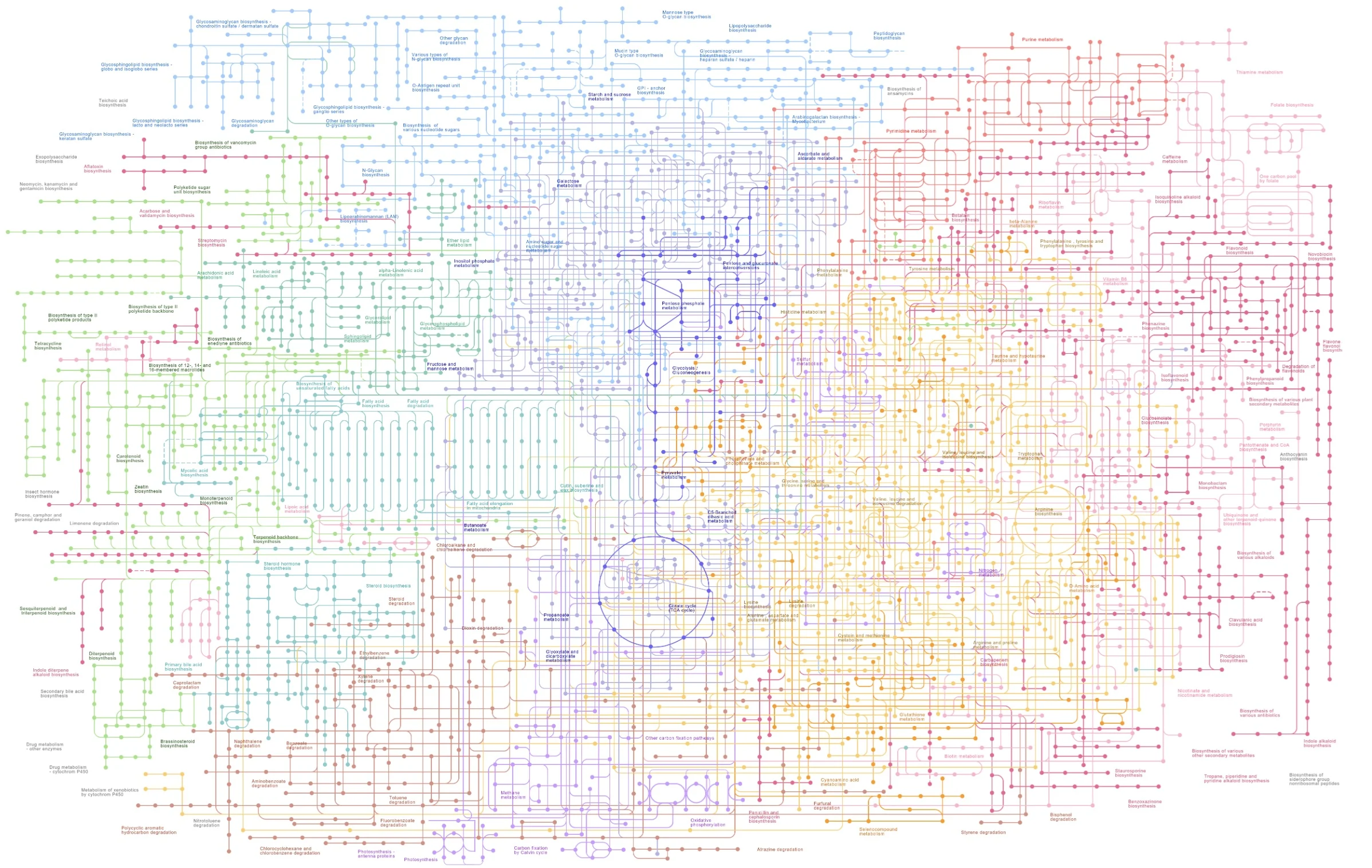
Metabolome Analysis
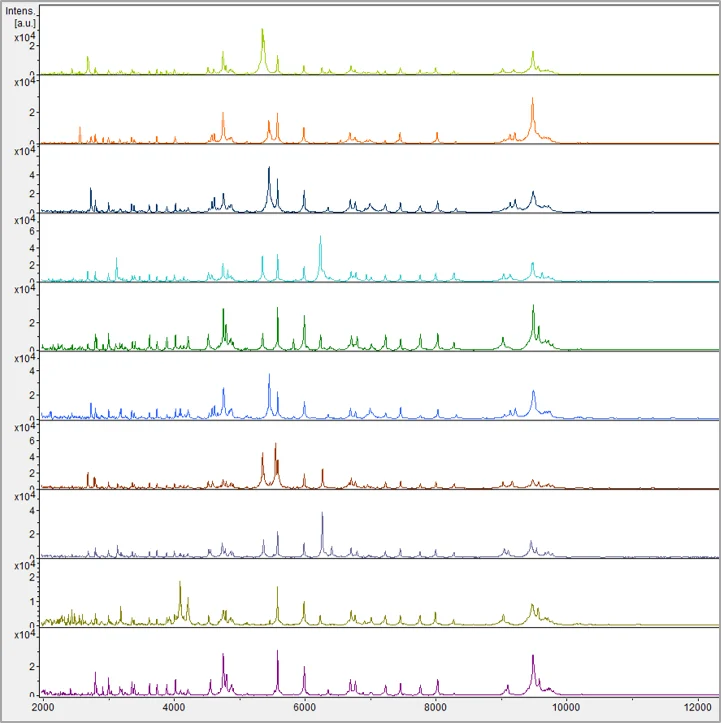
MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
Rapid strain identification is accomplished through high-throughput mass spectrometry technology.
Effectively improve the efficiency of strain screening,
Accelerate the development of functional strains for specific health goals.
Through high-throughput mass spectrometry technology, strain identification can be quickly completed, effectively improving strain screening efficiency and accelerating the development of functional strains oriented to specific health goals.
MALDI-TOF: Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Scaling Up Precision Fermentation
Leeuwenhoek Systematic Precision Fermentation Process
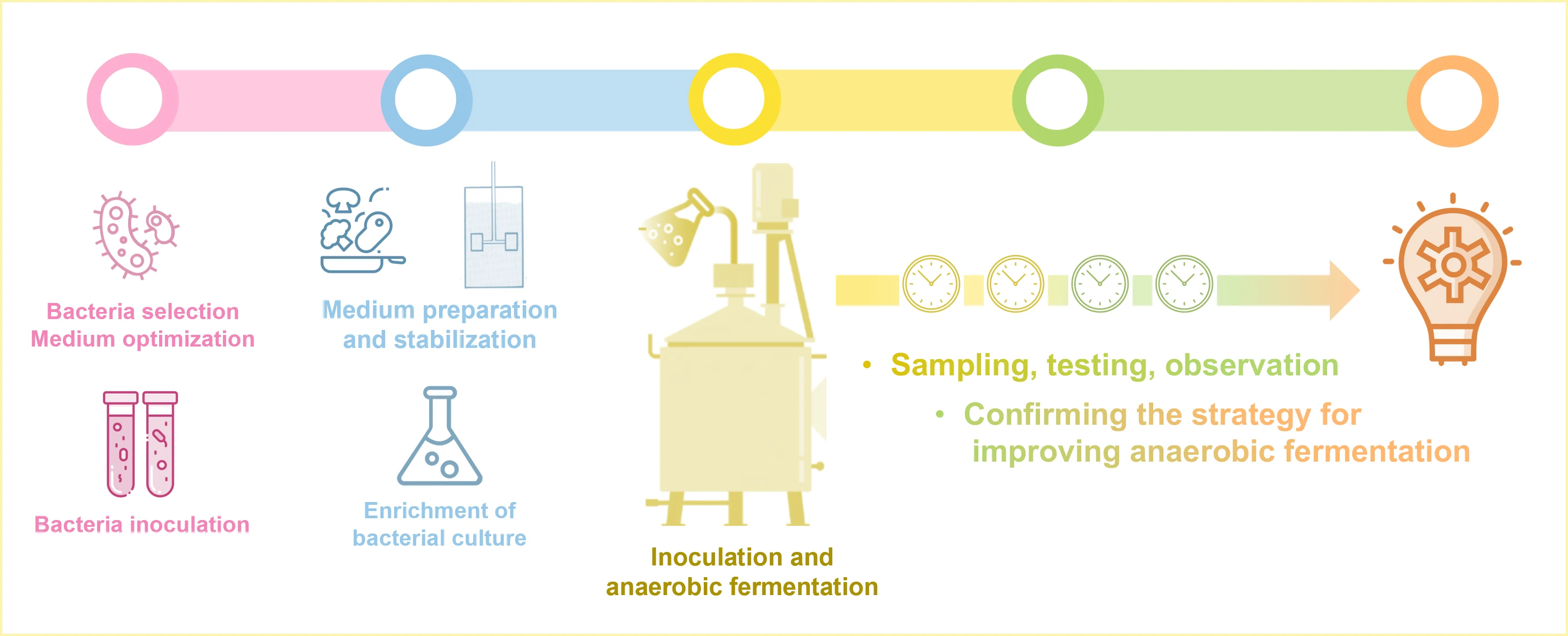
Applications & Product Development
Forms Available
- Live strains (strict anaerobic conditions required)
- Pasteurized strains (heat-treated, safe, stable)
- Cell-free extracts and postbiotics
Potential Applications
- Functional food and beverages
- Dietary supplements for metabolic health
- Gut barrier support and immune modulation
- Adjunct therapies for MAFLD, obesity, and diabetes
